External Adapter Encryption Keys
External Adapter functionality requires that data (potentially including PII Data - Personally Identifiable Information) is sent from the Fenergo platform to a downstream provider. Encryption and Authentication is required when sending such data outside our domain and clients can configure this as part of their Adapter Setup.
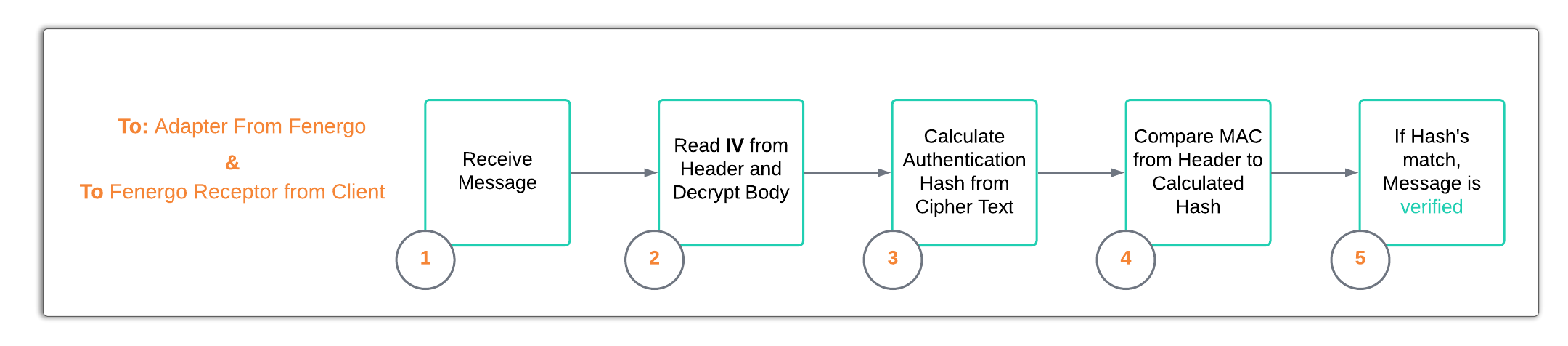
How the encryption and decryption are implemented is important to understand as Fenergo will call to a client adapter with the message body encrypted and authenticated. The client adapter must follow the Decryption Steps to read the messages and verify it originated from Fenergo. The client must then send the responses back following the same Encryption Steps. These steps are illustrated below at a high level and covered in detail within the External Adapter Encryption and Decryption Walkthrough.
Base 64 Keys
When using encryption, two keys are required, one for Encryption and one for Authentication. The Keys MUST be supplied as Base64 Encoded Strings
When you save and retrieve keys for your adapter to decode and authenticate messages or to encrypt and sign messages, ensure that you use the correct format. If you save and retrieve your Keys in the Base64 format, ensure you convert them back to byte[] arrays. In C# this done using Convert.FromBase64String(base64Key). Do NOT covert using Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(base64Key). This will not work.
Generate encryption keys to Secure Adapter
There are 2 keys required to implement the security.
- The First key, an Encryption Key, is used to encrypt the message body, and this is what is sent to the API endpoint inside the HTTP Body. As part of the encryption, an
IV(Initialization Vector) is also created and this is saved in a header calledx-encryption-iv. - The Second Key, an Authentication Key, is used to compute the HMAC Hash of the encrypted body. The computed hash is saved in a header called
x-authentication-mac.
You can find simple key generator on the web or below is a simple example which can create a base64 key using C#
Create Keys with C#
public string Generate256BitKey()
{
string base64Key = new string();
using (Aes aesAlgorithm = Aes.Create())
{
Console.WriteLine($"Aes Cipher Mode : {aesAlgorithm.Mode}");
Console.WriteLine($"Aes Padding Mode: {aesAlgorithm.Padding}");
Console.WriteLine($"Aes Key Size : {aesAlgorithm.KeySize}");
Console.WriteLine($"Aes Block Size : {aesAlgorithm.BlockSize}");
base64Key = Convert.ToBase64String(aesAlgorithm.Key);
Console.WriteLine($"Base64 Key : {base64Key}");
}
return base64Key;
}
The Output from the above code is below. The AES Key in Base64 encoding:
Aes Cipher Mode : CBC
Aes Padding Mode: PKCS7
Aes Key Size : 256
Aes Block Size : 128
Base64 Key : 4PNq6yXB0frFwQLeg77d8nI3R+tUyqqwsyEdZvgIzlI=
Create Keys with Python
Below is an example of the same key creation but using Python
import base64
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
def generate_256_bit_key():
base64_key = ""
with AES.new(keysize=256) as aes_algorithm:
printf("AES Cipher Mode: {aes_algorithm.mode}")
printf("AES Padding Mode: {aes_algorithm.padding}")
printf("AES Key Size: {aes_algorithm.key_size}")
printf("AES Block Size: {aes_algorithm.block_size}")
base64_key = base64.b64encode(aes_algorithm.key).decode("utf-8")
printf("Base64 Key: {base64_key}")
return base64_key
The Output from the above code is below. The AES Key in Base64 encoding:
AES Cipher Mode: CBC
AES Padding Mode: None
AES Key Size: 256
AES Block Size: 128
Base64 Key: PdzGMbtxQahJip09B4B7jQ==
Encryption Steps
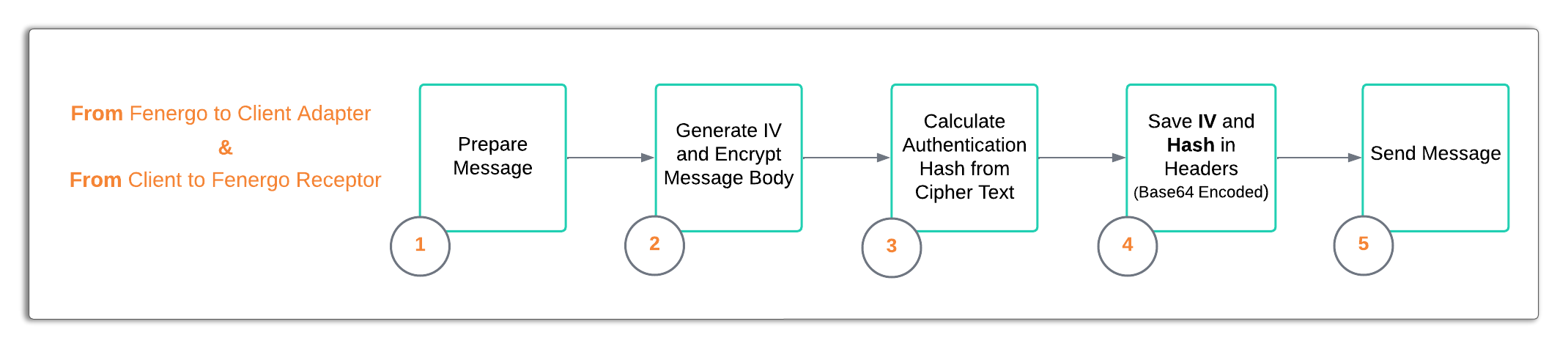
Decryption Steps