Custom Screening Provider
Screening Adapters allow you to submit clients and related entities to external Watchlists and Adverse Media screening providers, review of potential matches, and resolution of those matches. Fenergo integrates with three external screening providers: LexisNexis, GRID, and World‑Check One.
When a different provider is required, a Custom Screening Provider can be implemented.
Screening Adapter Templates
As a reminder Integration Flows does not implement a native screening flow type. Instead screening adapters are implemented using the API flow type. When configuring the Custom Screening Provider you will point it to invoke Integration Flow's Custom Authentication API Initiator.
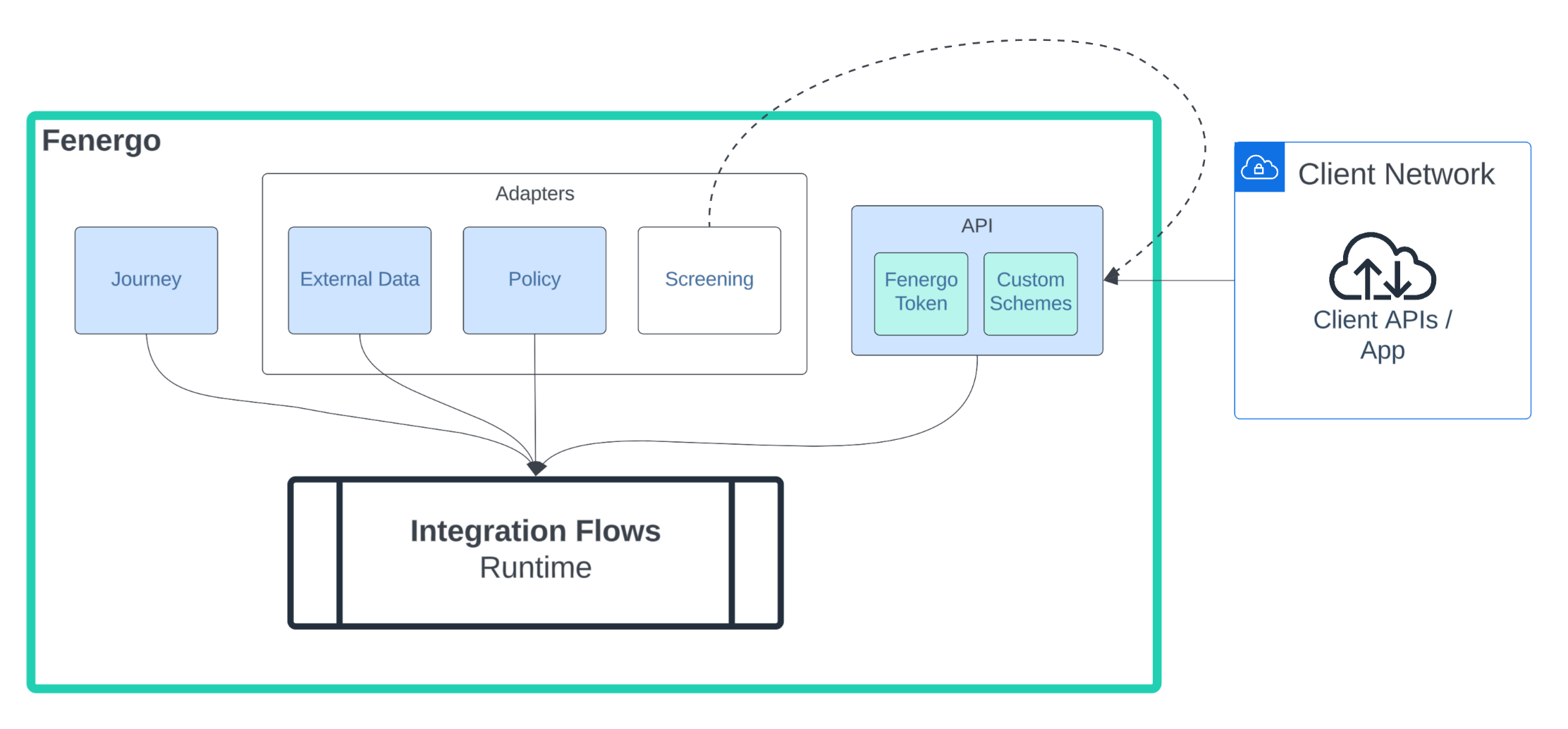
The Screening Provider Demo template provides a basic outline for building your own custom screening provider in Flows. It implements the three primary routes: Test, Screening, and Resolving Matches. Ongoing Screening is not included.
The overall design has been decomposed into five different templates to increase readability and avoid exceeding the maximum task transition limits in Flows. Combined, these templates create a custom adapter that can be integrated with your Journeys and then used to screen and resolve matches.
Templates:
- Screening Provider -or- Screening Provider with Encryption
- Screening Method Router
- Screening Test
- Screening Screen
- Screening Resolve Matches
This template implements a simplified version of the GRID screening adapter to illustrate best practices when implementing with Integration Flows, however it does take some shortcuts such as screening entities using only Legal Name. A fully-implemented adapter would use additional data points like registration IDs, custom resolving logic, etc...
1 - Screening Provider
The Screening Provider flow is the entry point of the custom screening adapter. It authenticates, and optionally decrypts the payload, before handing control to the Router via the Flow Invoker task. The last step returns the screening response to the Screening Receptor.
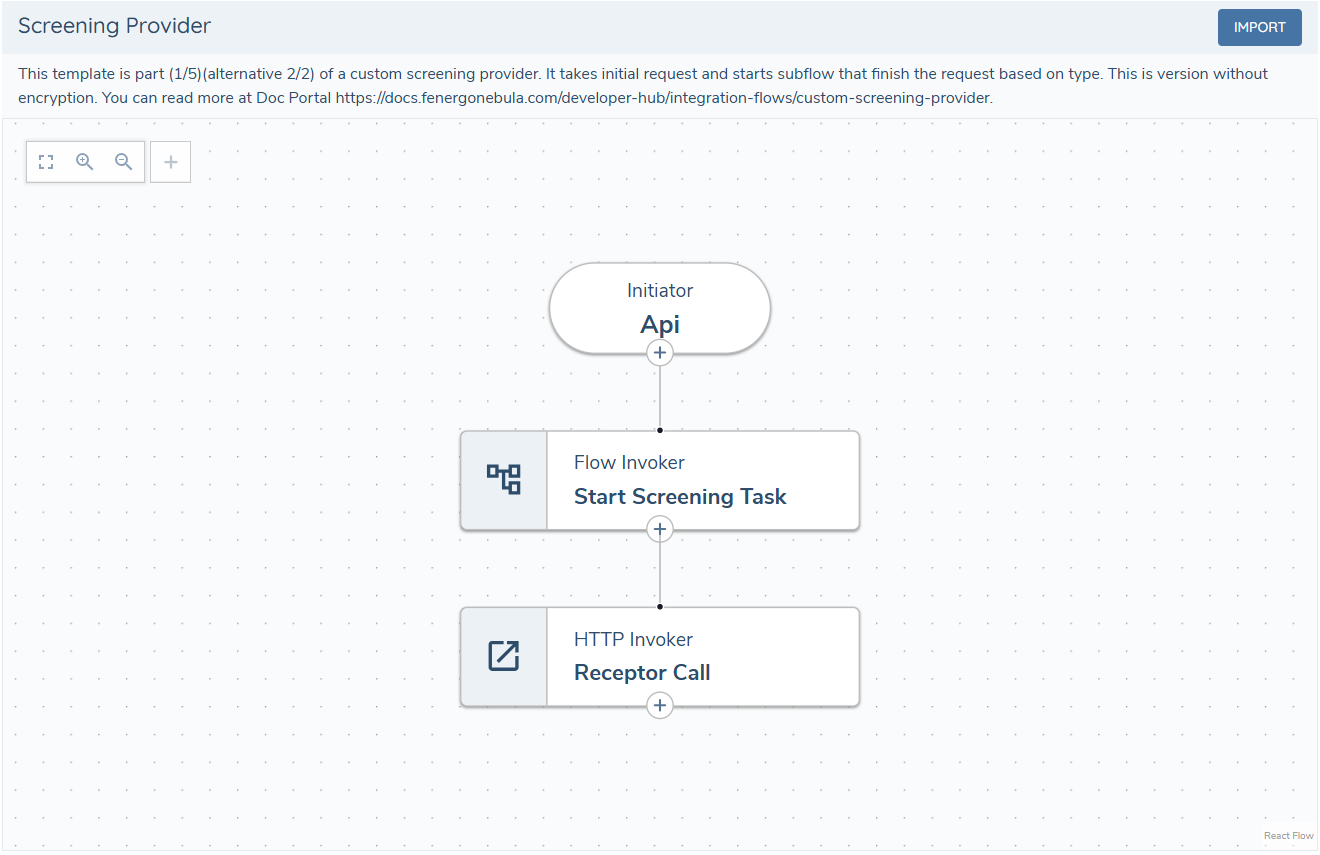
The receptor must always be called, even if an error occurs during processing. If not, the application user won't be notified of an issue and will have to wait for the request to time out.
Ensure that errors are handled throughout the process, and call the receptor with an appropriate error message.
Authentication
Screening Adapters use HMAC authentication which is natively supported in Integration Flows's Custom Authentication endpoint. Configure the same secret you use in your Screening Provider configuration.
As an additional security protection you can enable IP Whitelisting in the Flow's Custom Authentication configuration.
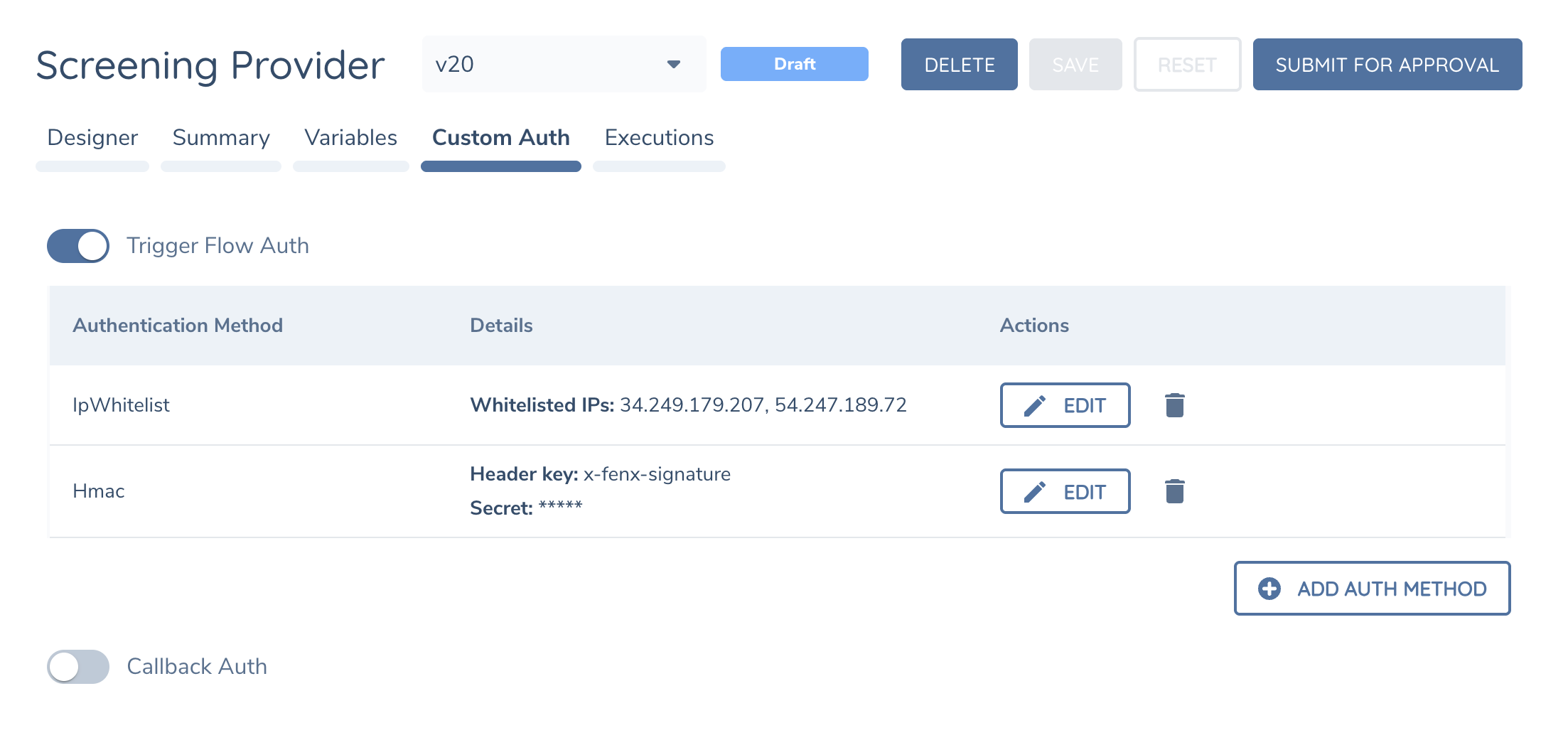
IP Ranges are specific to each region. Speak with Fenergo Support to confirm the IP Ranges in your region
Encryption
Screening Adapters can optionally encrypt payloads between the screening domain and adapter implementation. When implementing your screening adapter using Integration Flows the traffic does not leave Fenergo's network so encryption is not required but our templates includes it as an option (Screening Provider with Encryption).
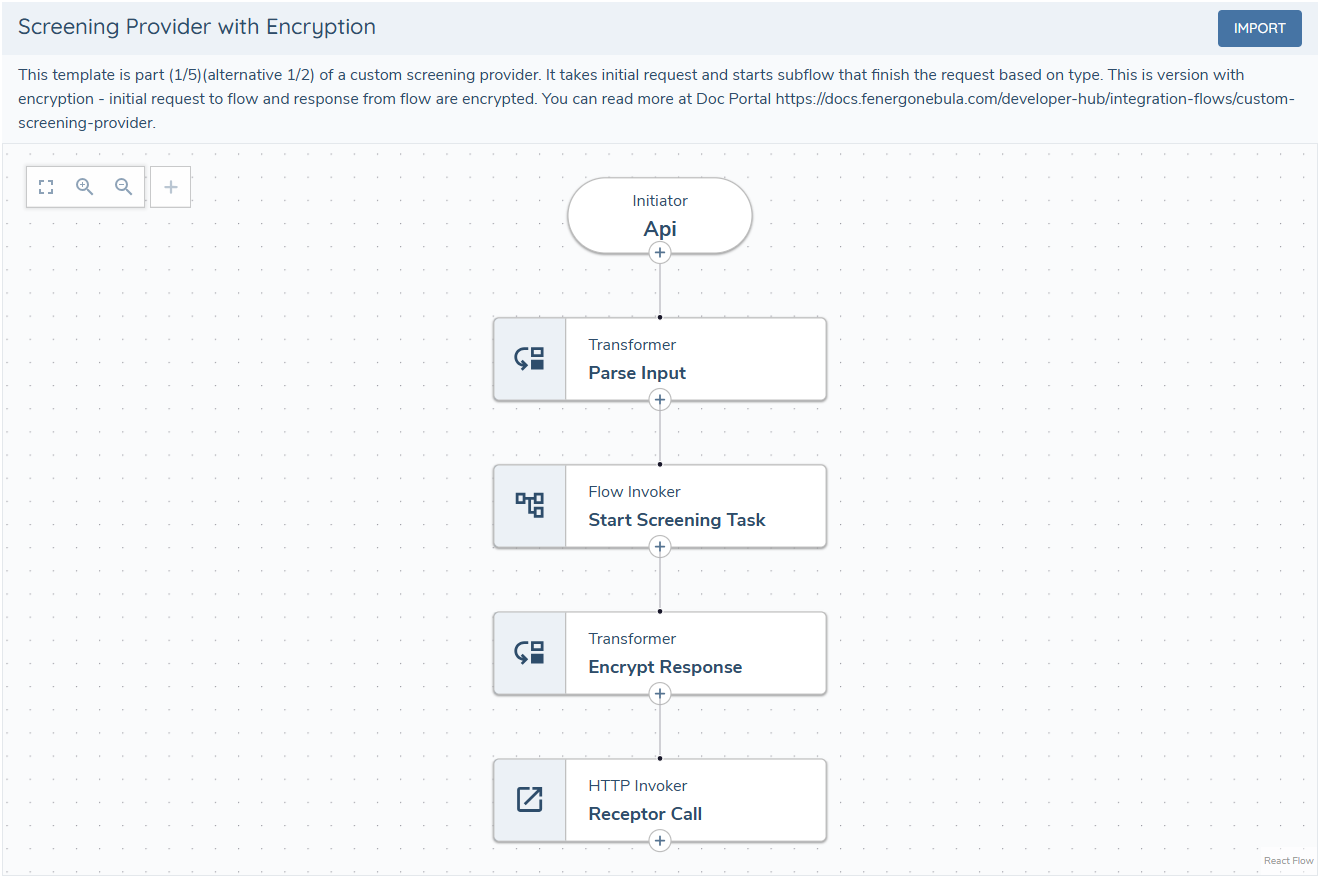
When encryption is enabled, two additional steps are required: decrypt the request and encrypt the response.
-
Decrypt the request — using the provided encryption and authentication keys, the request is decrypted and its authenticity verified.
function transform(input: InputObject): ResultObject {
// Get values from headers
const mac = input.headers?.['X-AUTHENTICATION-MAC']
const iv = input.headers?.['X-ENCRYPTION-IV']
const providerId = input.headers?.['X-PROVIDER-ID']
const tenantId = input.headers?.['X-TENANT-ID']
// context.crypto.aesDecrypt is a built-in function; it does not need to be implemented.
// Keys are hardcoded here for demonstration purposes; it is recommended to use flow/global secrets to store them.
const aesResult = context.crypto.aesDecrypt(input.bodyRaw, iv, mac, "OaBaSOn9lnxCeFNyKTg1jhWoy5DccTgXCffUhAn0hu4=", "OaBaSOn9lnxCeFNyKTg1jhWoy5DccTgXCffUhAn0hu4=")
if (!aesResult.authenticated) {
context.error("401", "Authentication failed")
}
request = JSON.parse(aesResult.plain)
return {
output: {
request: request
},
state: {
tenantId: tenantId,
providerId: providerId
}
};
} -
Encrypt the response — after processing the request, encrypt the response body.
function transform(input: InputObject): ResultObject {
// context.crypto.aesEncrypt is a built-in function; it does not need to be implemented.
// Keys are hardcoded here for demonstration purposes; it is recommended to use flow/global secrets to store them.
const encryptionResult = context.crypto.aesEncrypt(JSON.stringify(input.screeningResult), "OaBaSOn9lnxCeFNyKTg1jhWoy5DccTgXCffUhAn0hu4=", "qtLNwLunS/VLh1EaUJOjmH4H7pOBuSikobHqdbKdv1U=")
const response = encryptionResult.cipher as any
const iv = encryptionResult.IV
const mac = encryptionResult.mac
return {
output: {
response,
iv,
mac
},
state: {}
};
}
To enable encryption, configure the following in your screening provider:
adapterConfiguration.authenticationActive— bool — enables encryption. When true, the request requires decoding, and the response sent to the receptor requires encoding.adapterConfiguration.authenticationKey.key— string — Base64‑encoded 32‑byte key used for HMAC‑SHA256 signing and verification.adapterConfiguration.encryptionKey.key— string — Base64‑encoded 32‑byte key used for HMAC‑SHA256 encoding.
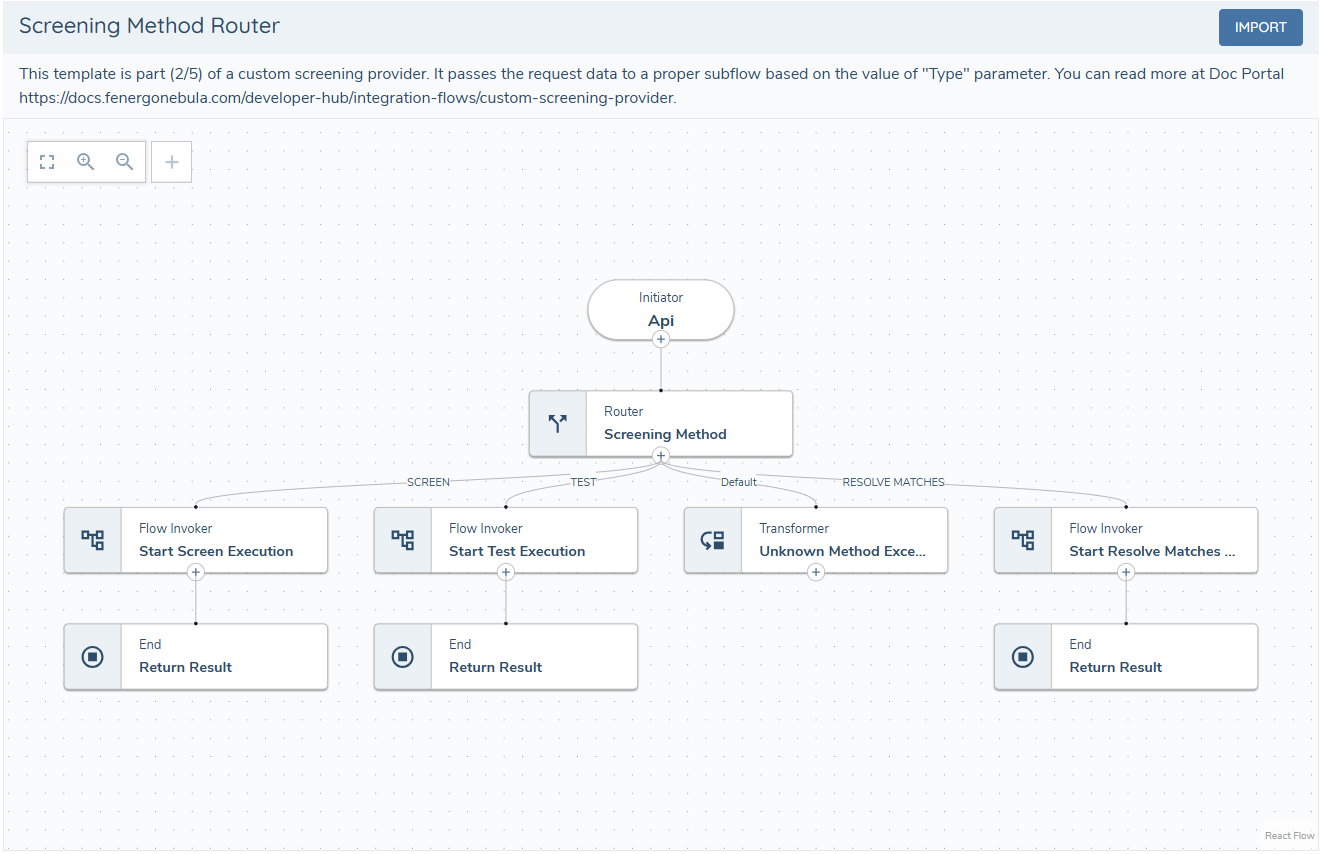
2 - Task Routing
This flow checks the request type and handles branching based on message type: Test, Screen, or ResolveMatches.
As shown, the default path does not return any response - it throws an exception in the transformer task. There is no need to return a response to the receptor if the message is not recognized and is outside the scope of the provider.
3 - Test Task
The contents of this flow are optional and are not part of the screening process. This subflow is part of the custom provider configuration and is used to verify and enable it. It is recommended to use it to test connectivity to the provider, validate credentials, or perform any other checks needed to verify that the provider is working.
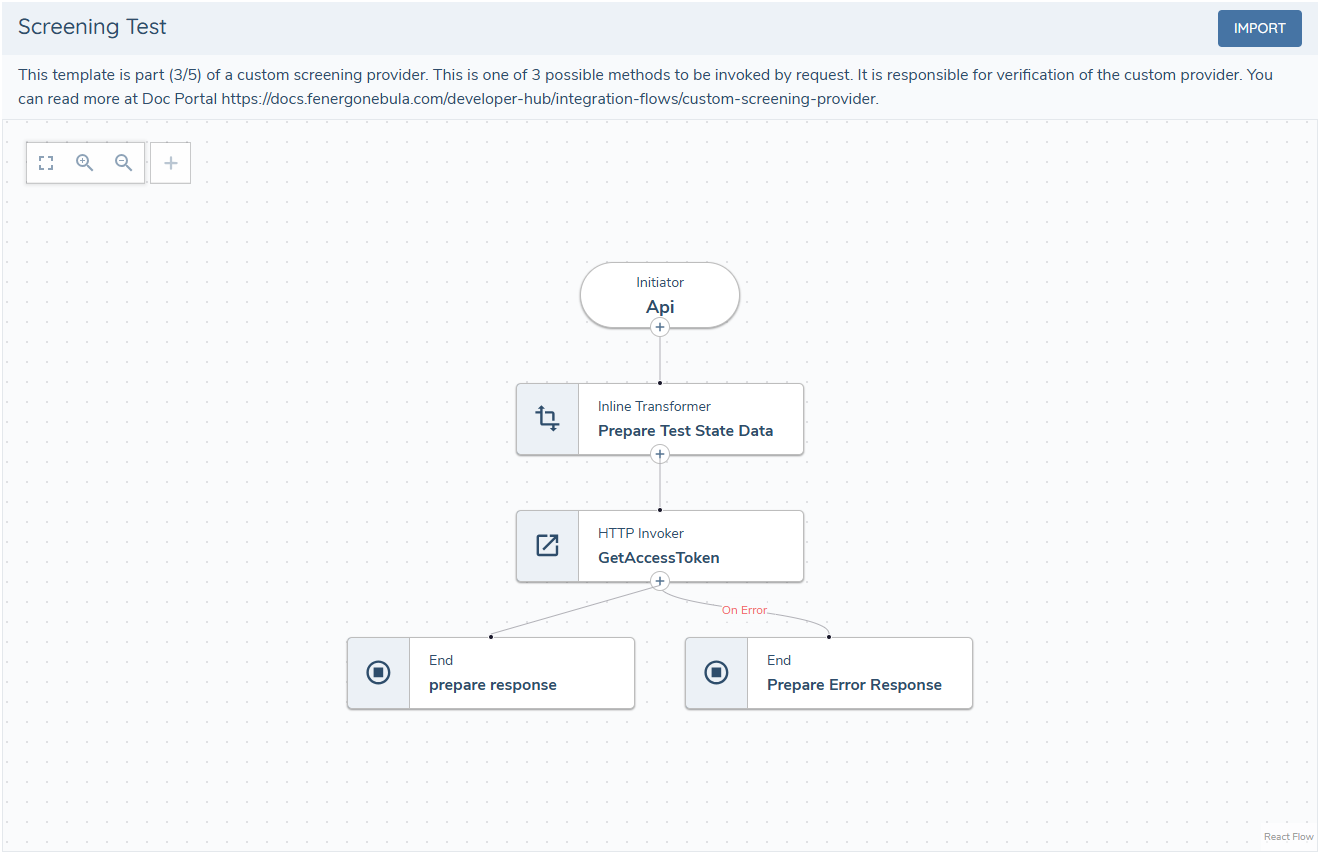
More about the test response can be found screening receptor documentation.
4 - Screening Task
This subflow finds entities that match the search criteria and returns a response ready for the receptor call. Implementation details depend on the provider API. It is important to always return a response to the receptor at every step that is prone to errors.
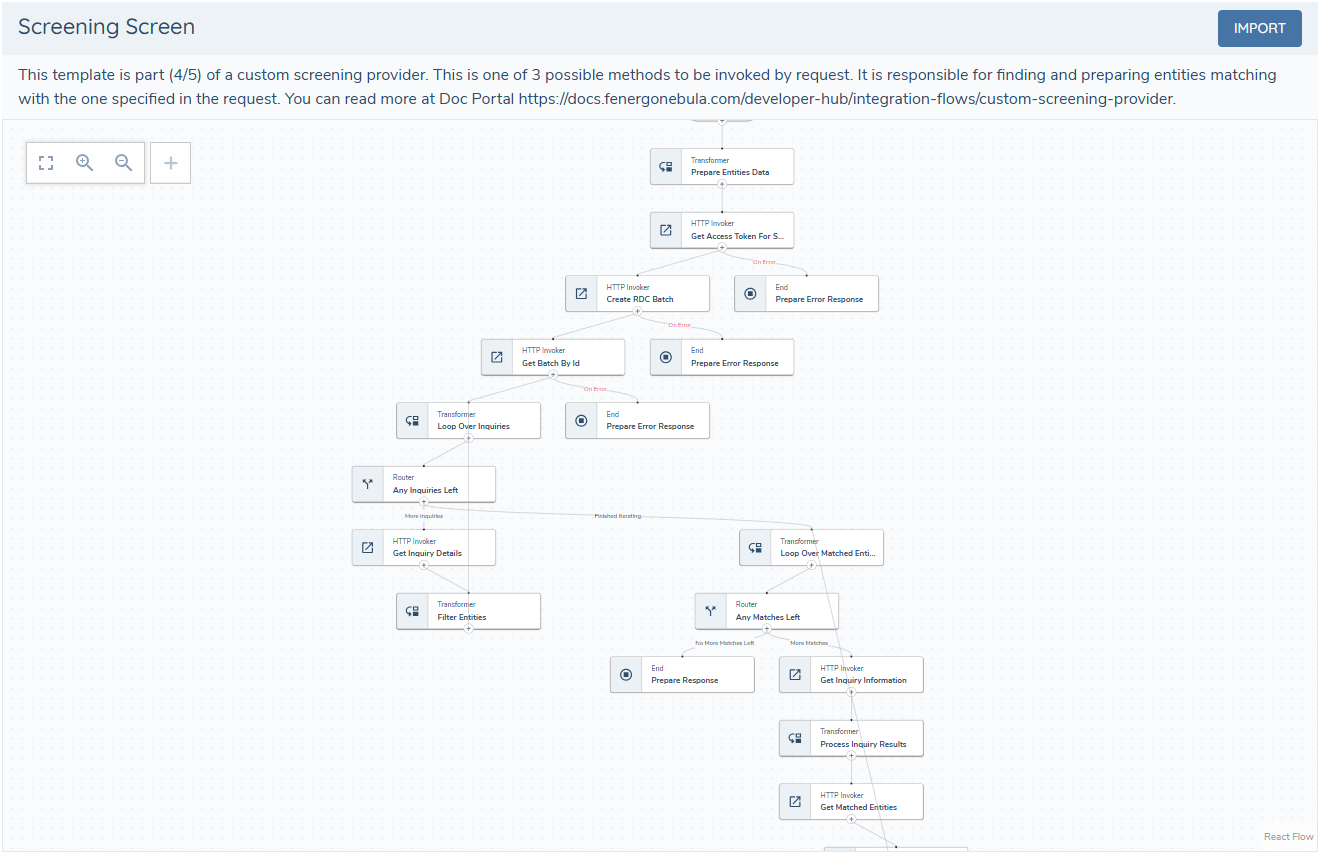
More about the screening response can be found screening receptor documentation.
5 - Resolve Matches Task
This subflow resolves matches previously returned by the screening task. It is used to update match status (true match, false positive). Implementation details depend on the provider API.
It is important to always return a response to the receptor at every step that is prone to errors.
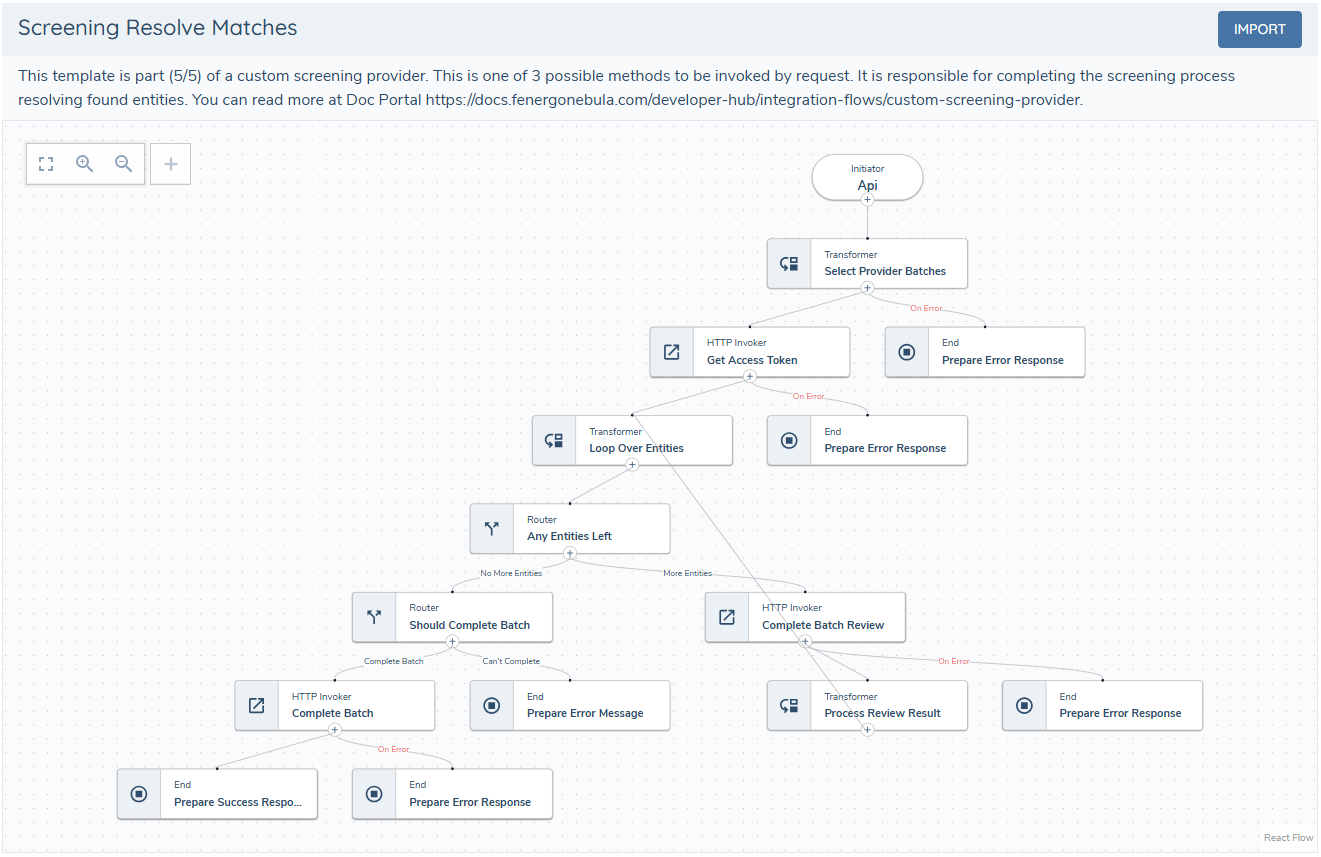
More about the resolve matches response can be found in screening receptor documentation.
Configuration
For general information on the Custom Screening Provider.
For flows, the url field should point to the flow initiator endpoint for your environment: e.g. https://app.fenergox.com/integrationcore/api/execution/flow/{FlowId or FlowKey}/ (API docs, initiator docs).