SQL
This section explores some SQL resources and some tips to keep in mind when querying Fenergo SaaS data.
Resources
Some familiarity with SQL will greatly improve the quality of data that is returned in a report. This user guide will not cover how to learn SQL, but here are some resources to help:
For complete beginners, start here.
For those with previous experience looking to refresh their knowledge, this short game is a good resource to practice translating questions into queries.
Fenergo SaaS uses a version of SQL called Presto. For detailed information on Presto-specific functions, please see the Presto Documentation.
For those who want to use some pre-written queries without learning SQL, go to the Example Queries section in this document.
Quick Tips
These are some tips to keep in mind when querying inside Fenergo SaaS.
Sub-Tables
Your tables are listed on the left of the query editor. If a table is a sub-table of a domain (for example the datagroup "addresses" belongs to the entitydata domain), it can be accessed using an underscore: "entitydata_addresses"
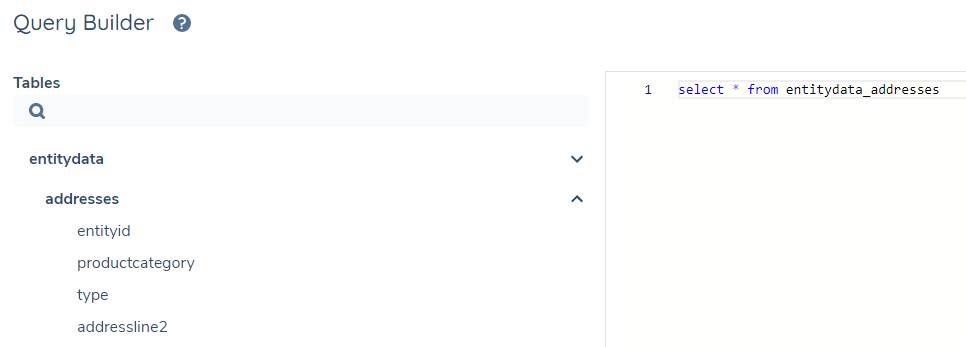
Other sub-tables include:
- journey_milestones
- journey_stages
- journey_processes
- journey_tasks
Handling Multi-Valued Data Types
Arrays
Some data fields in the table are arrays that contain a list of information. The data inside of them can be accessed using array operators. For an extensive overview of Array functions and how to use them, see the Presto Documentation
An entry for "countries" may be ["Greece", "Ireland", "United Kingdom"]
You can check if "Ireland" is in the array with the notation contains(countries, "Greece")
SELECT * FROM entitydata_addresses WHERE contains(countries, "Greece")
Rows
Some data fields in the tables contain layers of information that are organised as ROW objects. The data inside of them can be accessed using special operators. For information on the ROW type, see the Presto Documentation.
An entry for "accesslayers" may be "{businessrelated=[Enterprise], geographic=[Global]}"
To investigate a key inside of the object, use the notation "accesslayers.businessrelated"
SELECT accesslayers.businessrelated FROM entitydata
Handling Numbers
Some data may appear numeric, but is actually a string. Failing to account for this may result in mathematical operations failing or producing inaccurate information (for example 5+5=10, while "5" + "5" = "55"). This means they must be cast to numbers to produce accurate results.
To check the type of a field you are unsure of, use typeof() or see the Data Type column above in this guide.
SELECT typeof(ownershippercentage) FROM relatedparties
To cast a string, use cast(value AS type), substituting "value" for your data point, and "type" for the datatype.
SELECT * FROM entitydata WHERE cast(income AS DOUBLE) > 15000
Handling Dates
Some data fields may present as dates/timestamps but are strings. Converting these types to actual date objects means a wider range of functions can be applied to them. They can be converted and managed using date operators. The dates defined in your policy may have a different formats. The Presto docs above can help guide how to convert different input types.
Most timestamps in the reporting feature use the iso8601 format. They can be converted using from_iso8601_timestamp(string)
SELECT * FROM entitydata WHERE from_iso8601_timestamp(created) > cast('2021-08-31' AS DATE)
Example Queries
The headings below ask some business questions that can be answered using SQL queries. When testing these, please note that some of the datakeys and values used in these queries may differ per tenant.
Data Groups
SELECT * FROM entitydata
This is the most basic SQL query. It is useful for exporting all unfiltered/non-aggregated data into a CSV file, where further analysis can be executed elsewhere.
SELECT
*
FROM
entitydata
LEFT JOIN entitydata_addresses ON entitydata.id = entitydata_addresses.entityid
LEFT JOIN entitydata_contacts ON entitydata.id = entitydata_contacts.entityid
To add more datagroups, continue to add LEFT JOIN datagroupdatakey ON entitydata.id = datagroupdatakey.entityid to the end of the query
SELECT
*
FROM
journey
LEFT JOIN entitydata ON journey.entityid = entitydata.id
LEFT JOIN entitydata_addresses ON journey.entityid = entitydata_addresses.entityid
LEFT JOIN entitydata_contacts ON journey.entityid = entitydata_contacts.entityid
To add more datagroups, continue to add LEFT JOIN datagroupdatakey ON entitydata.id = datagroupdatakey.entityid to the end of the query
Dates and Times
SELECT
*
FROM
journey
WHERE
from_iso8601_timestamp (completed) >= date ('2022-06-01')
- Convert the 'completed' string into a date, so it can be compared accurately
- Filter by all dates that are greater than June 1st 2022
- Convert the string '2022-06-01' into a date. Just typing '2022-06-01' will be recognised as a string, but converting it means it will be recognised as June 1st 2022 00:00:00 am
SELECT
*
FROM
journey
WHERE
from_iso8601_timestamp (started) >= date ('2022-06-01')
AND from_iso8601_timestamp (started) <= date ('2022-08-31')
Relatated Parties
SELECT
targetid,
Count(*) AS numberofshareholders
FROM
relatedparties
WHERE
type = 'Shareholder'
GROUP BY
targetid
- Group by targetid (the entity that is the target of the ownership)
- Count the number of relationships that entity has, and call the column 'numberofsharholders'
- Filter so only relationship types of "Shareholder" are counted
SELECT
targetid,
Sum(Cast(ownershippercentage AS DOUBLE)) AS totalownership
FROM
relatedparties
GROUP BY
targetid
- Group by targetid (the entity that is the target of the ownership)
- Convert ownershippercentage to a number
- Sum all the ownershippercentage results together to get total known ownership for that entity/targetid
SELECT
targetid,
SUM(CAST(ownershippercentage as DOUBLE)) AS totalownership,
CASE
WHEN SUM(CAST(ownershippercentage as DOUBLE)) = 0 THEN 'No ownership known'
WHEN SUM(CAST(ownershippercentage as DOUBLE)) = 100 THEN 'Full ownership known'
ELSE 'Some ownership known'
END AS ownershipflag
FROM
relatedparties
GROUP BY
targetid
- The CASE statement in this query allows us to assign an outcome dependent on other data points
- First, calculate the totalownership for each target
- Use this calculation to populate a new column 'ownershipflag' that describes how much ownership is known
SELECT
relatedparties.sourceid AS OwnsRussianEntity,
relatedparties.type,
entitydata.id AS RussianEntity
FROM
relatedparties
JOIN entitydata ON relatedparties.targetid = entitydata.id
WHERE
entitydata.countryofincorporation = 'Russia'
- List out the source entity IDs - these represent the entities who own a Russian entity
- List the relationship type to provide context on the type of ownership
- Join the entity data for the target IDs, and check that data for a 'countryofincorporation' that is Russia
- List the entity IDs of the Russian entities
- Since we joined on targetid = entityid, the entitydata.id represents the 'owned'/'target' entity
Access Layers
SELECT
*
FROM
entitydata
WHERE
contains (accesslayers.geographic, 'Spain')
- Select just the geographic portion of the accesslayers data point: accesslayers.geographic
- Check is 'Spain' is contained anywhere in that list of geographic access layers
SELECT
id,
legalentityname
FROM
entitydata
WHERE
riskLevel = 'High'
and nationality = 'France'
- Select just the columns "ID" and "Legal Entity Name"
- Filter so that only entities that are High Risk and from France appear in the report
SELECT DISTINCT(nationality) FROM entitydata
- Get all the nationality data points in entity data, and list all the unique values
Journey
SELECT status, COUNT(*) FROM journey GROUP BY status
- Group all journeys by their status
- Count the number of journeys in each of these groups
SELECT
entitydata.id
FROM
entitydata
WHERE
entitydata.id NOT IN (
SELECT
relatedparties.targetid
FROM
relatedparties
)
AND entitydata.id NOT IN (
SELECT
relatedparties.sourceid
FROM
relatedparties
)
AND entitydata.id NOT IN (
SELECT
journey.entityid
FROM
journey
)
- First, make 3 lists:
- Entities that are "targets" (have a related party 'owning'/'targeting' them)
- Entities that are "sources" ('own' another entity)
- A list of entities that have a journey
- Then check for all the entities that exist in the entity list, but not in any of these lists
SELECT
id,
entityid,
cancelled,
cancelledby,
cancellationcomment
FROM
journey
WHERE
cancelled IS NOT NULL
- Select a subset of attributes that give information about journey cancellations
- Filter the results to only show journeys that were cancelled
SELECT
journey.id,
journey.entityid,
journey.type,
journey.status,
journey.completed
FROM
journey
WHERE
journey.status = 'Done'
AND journey.type = 'Client Onboarding'
- Choose only the 'Done' journeys
- Filter so only the 'Client Onboarding' types are listed
Journey Metadata
SELECT
*,
From_iso8601_timestamp (completed) - From_iso8601_timestamp (started) AS timetaken
FROM
journey
- Select everything
- Create a new column that calculated a difference between the time completed and the time started
SELECT
type,
Avg(
From_iso8601_timestamp (completed) - From_iso8601_timestamp (started)
) AS timetaken
FROM
journey
GROUP BY
type
ORDER BY
timetaken DESC
- Calculate the time taken to complete each journey
- Group each journey by type - ie. grouping "Client Onboarding" or "Regular Review" together
- Get the average time taken across these groups
- List the groups from highest average time to lowerst average time
SELECT
team.NAME,
teamtasks.totaltaskscompleted,
teamtasks.timespent
FROM
(
(
SELECT
teamid,
Count(*) AS totaltaskscompleted,
Sum(
From_iso8601_timestamp (completed) - From_iso8601_timestamp (started)
) AS timespent
FROM
journey_tasks
WHERE
iscompleted = true
GROUP BY
teamid
) AS teamtasks
)
LEFT JOIN team ON team.id = teamtasks.teamid
- Select only the completed tasks
- Group by teamid
- Calculate how much time was spent on each task
- Sum each time taken to get the total number of hours spent per team
SELECT
*
FROM
journey
WHERE
status = 'Done'
AND journeyschemaversionnumber = 3
AND name = 'Client Onboarding'
- Filter by journey status being 'Done'
- Filter again by journeyschemaversionnumber. Since this field is a number, it does not need 'quotes'
- Filter again by the type of journey that it is
SELECT
USER.username,
usercompleted.numberoftaskscompleted
FROM
(
(
SELECT
completedby,
Count(*) AS numberoftaskscompleted
FROM
journey_tasks
GROUP BY
completedby
) AS usercompleted
)
LEFT JOIN USER ON USER.id = usercompleted.completedby
- Group the journey tasks table by the user ID of who completed it
- Count the number of tasks that exist in each of those groups
- Rename the count column to numberoftaskscompleted
SELECT
USER.username,
averagetimeuser.averagetimetaken
FROM
(
(
SELECT
completedby,
Avg(
From_iso8601_timestamp (completed) - From_iso8601_timestamp (started)
) AS averagetimetaken
FROM
journey_tasks
WHERE
status = 'Done'
GROUP BY
completedby
) AS averagetimeuser
)
LEFT JOIN USER ON USER.id = averagetimeuser.completedby
- Group all completed tasks by the user that completed it
- For each of these groups, calculate the average time it took to compelete all this user's tasks
SELECT
type,
Avg(
From_iso8601_timestamp (completed) - From_iso8601_timestamp (started)
) AS timetaken
FROM
journey
WHERE
From_iso8601_timestamp (started) >= Date ('2022-05-01')
AND From_iso8601_timestamp (started) <= Date ('2022-05-31')
GROUP BY
typeselect type,
avg(
from_iso8601_timestamp (completed) - from_iso8601_timestamp (started)
) AS timetaken
FROM
journey
WHERE
from_iso8601_timestamp (started) >= date ('2022-05-01')
AND from_iso8601_timestamp (started) <= date ('2022-05-31')
GROUP BY
type
- Group all journeys by their type
- Filter to only return journeys that started in May 2022
- Across these groups, calculate the average time it took to complete each type of journey
SELECT
Date_trunc ('month', From_iso8601_timestamp (completed)) AS month,
Count(*) AS journeyscompleted
FROM
journey
WHERE
status = 'Done'
AND From_iso8601_timestamp (completed) > Cast('2021-12-31' AS DATE)
GROUP BY
Date_trunc ('month', From_iso8601_timestamp (completed))
- The date_trunc() function takes a detailed timestamp and simplifies it down to one unit - in this case, just the month.
- For example, 2022-09-13T15:05:44.8713428Z and 2022-09-30T07:35:51.2772693Z are different timestamps, but date_trunc('month', timestamp) simplifies them both to the same month - 2022-09-01 00:00:00
- The query above groups all the completed journeys (after 2021) by the month they were completed, and counts the number of journeys in each group
select
journey.id as journeyID,
journey.name as JourneyName,
journey_tasks.name as TaskName,
current_timestamp - from_iso8601_timestamp (journey_tasks.servicelevelagreement.duedate) as OverdueBy
from
journey_tasks
LEFT JOIN journey on journey_tasks.journeyid = journey.id
WHERE
from_iso8601_timestamp (journey_tasks.servicelevelagreement.duedate) < current_timestamp
AND journey.status = 'In Progress'
- Every task in an in-progress journey that is in breach of its SLA
Security
SELECT
*
FROM
(
(
SELECT
username,
Array_join (Array_agg (teamname), ', ') AS teams
FROM
(
SELECT
USER.username,
teamnames.NAME AS teamname
FROM
USER
LEFT JOIN (
(
SELECT
team_user.userid,
team.NAME
FROM
team
LEFT JOIN team_user ON team_user.teamid = team.id
) AS teamnames
) ON teamnames.userid = USER.id
)
GROUP BY
username
) AS tnames
)
JOIN (
(
SELECT
username,
array_join (array_agg (accesslayers), ', ') AS accesslayers
FROM
(
SELECT
als.username,
concat (
accesslayer.label,
' - ',
accesslayer.type,
' - ',
accesslayer.datatype
) AS accesslayers
FROM
(
(
SELECT
USER.username,
accesslayer_user.accesslayerid
FROM
USER
LEFT JOIN accesslayer_user ON accesslayer_user.userid = USER.id
) AS als
)
JOIN accesslayer ON accesslayer.id = als.accesslayerid
)
GROUP BY
username
) AS alayers
) ON alayers.username = tnames.username
All users in the system and a complete summary of all their access layers and teams.
SELECT
scope,
Array_join (Array_agg (username), ', ') AS users
FROM
(
SELECT
scope,
username
FROM
(
(
SELECT
scope,
userid
FROM
(
(
SELECT
id,
NAME,
scope
FROM
team
CROSS JOIN Unnest (scopes) AS t (scope)
) AS scopetable
)
LEFT JOIN team_user ON team_user.teamid = scopetable.id
) AS scopeusers
)
LEFT JOIN USER ON USER.id = scopeusers.userid
)
GROUP BY
scope
Every permission/action in the tenant and what users are allowed to perform that action
Products
SELECT
e.id AS entityid,
COALESCE(
e.legalentityname,
Concat (e.firstname, ' ', e.lastname),
e.id
) AS entityname,
p.*
FROM
relatedparties rp
LEFT JOIN product p ON p.productid = rp.targetid
LEFT JOIN entitydata e ON e.id = rp.sourceid
WHERE
rp.type = 'product'
AND p.productid IS NOT NULL
Every entity that has a product (it's ID and legal entity name) along with all product information. In order to link entities to product, users must use the relatedparties table to find the product-entity association.
SELECT
type,
productriskrating,
Count(*) AS numberofproducts
FROM
product
WHERE
productriskrating IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY
type,
productriskrating
ORDER BY
numberofproducts DESC
Product grouped by their risk level, with a count of how many product/risk combinations exist.
The above query uses productriskrating as a datakey, but this may be different per tenant.
Deals
SELECT
e.type AS entityType,
COALESCE(
e.legalentityname,
Concat (e.firstname, ' ', e.lastname),
e.id
) AS entityname,
de.*
FROM
deals de
INNER JOIN entitydata e ON e.id = de.entityid
WHERE
e.id = 'ENTITY_ID'
ORDER BY
de.created
Returns all deals associated with a specific entity. Entity details are pulled from the entitydata table using the entityid field in the deals table.
SELECT
e.type AS entityType,
COALESCE(
e.legalentityname,
Concat (e.firstname, ' ', e.lastname),
e.id
) AS entityname,
de.*
FROM
deals de
INNER JOIN entitydata e ON e.id = de.entityid
INNER JOIN journey jn ON jn.entityid = e.id
WHERE
e.id = 'ENTITY_ID'
AND de.created <= '2026-03-12T03:39:15.168Z'
AND de.created >= '2023-03-12T03:39:15.168Z'
ORDER BY
de.created DESC
All deals for a given entity that were created within a specific date range. This query also joins the journey table to ensure the entity has an associated journey. Adjust the timestamps as needed.
SELECT
e.type AS entityType,
COALESCE(
e.legalentityname,
Concat (e.firstname, ' ', e.lastname),
e.id
) AS entityname,
de.*
FROM
deals de
INNER JOIN entitydata e ON e.id = de.entityid
INNER JOIN relatedparties rp ON rp.sourceId = de.dealid
AND rp.type = 'dealProduct'
INNER JOIN product pr ON rp.targetid = pr.productid
AND pr.type = 'PRODUCT_TYPE'
WHERE
e.id = 'ENTITY_ID'
ORDER BY
de.created
Returns all deals for a given entity that are associated with a specific product type. The relationship between deals and products is managed via the relatedparties table, using dealProduct as the linking type.
Screening
SELECT DISTINCT
se.id,
se.legalentityid,
se.searchcriteria.legalentityname,
se.searchcriteria.firstname,
se.searchcriteria.lastname,
provider.providerid,
provider.ongoingscreeningenabled,
provider.configurationsetid
FROM screening_entities se
CROSS JOIN UNNEST(se.ongoingscreeningproviders) AS t(provider)
WHERE provider.ongoingscreeningenabled = true
AND se.issoftdeleted = false
ORDER BY se.legalentityid, provider.providerid;
SELECT
m.id AS match_id,
m.legalentityid,
m.batchid,
m.status AS match_status,
m.reason,
m.name AS matched_entity_name,
m.categories,
m.matchscore,
m.providerid,
b.createddate,
b.journeyid
FROM screening_matches m
JOIN screening_batches b ON m.batchid = b.id
WHERE (
ARRAY_JOIN(m.categories, '|') LIKE '%Sanctions%'
)
AND b.createddate >= '2023-01-01'
AND b.createddate <= '2025-08-01'
AND m.status = 'Match'
ORDER BY b.createddate DESC;
SELECT
sm.id AS match_id,
sm.status AS match_status,
sm.reason AS match_reason,
sm.legalentityid AS entity_id,
sm.batchid AS batch_id,
sb.createddate AS batch_created_date,
sb.status AS batch_status,
COALESCE(
sbe.searchcriteria.legalentityname,
'Unknown Entity'
) AS entity_name,
sm.categories AS match_categories,
sm.providerid,
sb.createddate AS created_date_for_filtering
FROM screening_matches sm
JOIN screening_batches sb ON sm.batchid = sb.id
JOIN screening_batchentities sbe ON sm.batchentityid = sbe.id
LEFT JOIN screening_entities se ON sm.legalentityid = se.legalentityid
WHERE
sm.status IN ('Unresolved', 'PotentialMatch')
AND sb.createddate < '2024-11-01'
AND sb.status = 'Open'
AND (se.issoftdeleted = FALSE OR se.issoftdeleted IS NULL)
ORDER BY sb.createddate ASC;